The pepper in all its forms


History and Botany
The pepper, or Capsicum annuum, originates from the heart of the highly fertile Amazon basin, one of the richest natural reserves on Earth. Quickly, as birds are insensitive to its burning effect, pepper transitioned and proliferated throughout South America, Central America, and Mexico.
The consumption of pepper seems to date back to around 7000 BC. It was used by pre-Columbian civilizations to spice up their dishes. Pepper arrived in Europe following the discovery of the Americas by Christopher Columbus. Captivated by the organoleptic qualities of pepper, the explorer brought it back to Europe as a substitute for the expensive pepper of the time.
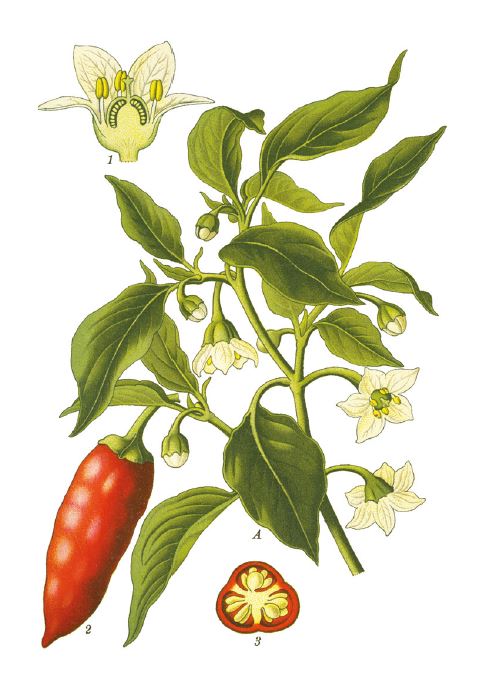
The pepper family includes bell peppers, paprika, and hot peppers. They all belong to the botanical branch of Solanaceae, just like tomatoes, potatoes, and eggplants. The cultivated cultivation of pepper has given rise to various varieties. Today, nearly 2,300 varieties of pepper are listed in the European catalog of species and varieties.
Among these varieties, five major species of Capsicum stand out: annuum, baccatum, chinense, frutescens, and pubescens.


The cultivation of peppers

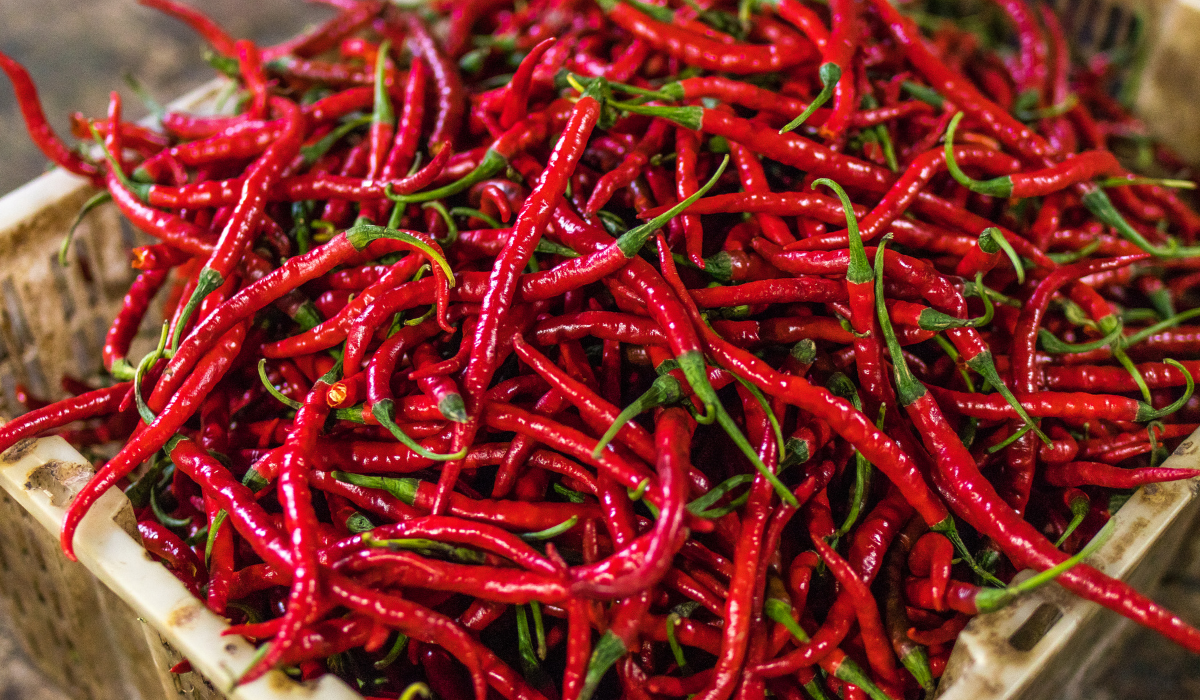
The cultivation of peppers is primarily done in warm and oceanic climates. Peppers require a lot of heat to thrive and cannot tolerate frost. They particularly thrive in soils that are rich in humus, loose, and deep, allowing for the development of their powerful root system, which can reach depths of up to 90 cm. Peppers also require ample sunlight.
The cultivation of peppers is similar to that of vineyards. Factors such as soil geology, plot exposure, row orientation, and weather conditions have a strong impact on the quality and flavors of peppers. Peppers are typically green and turn red when they ripen. They are mostly harvested at this stage, but they can also be picked and consumed before they fully turn red.
In France, particularly in Espelette, pepper harvesting begins in August and lasts until early December, before the first frosts occur.

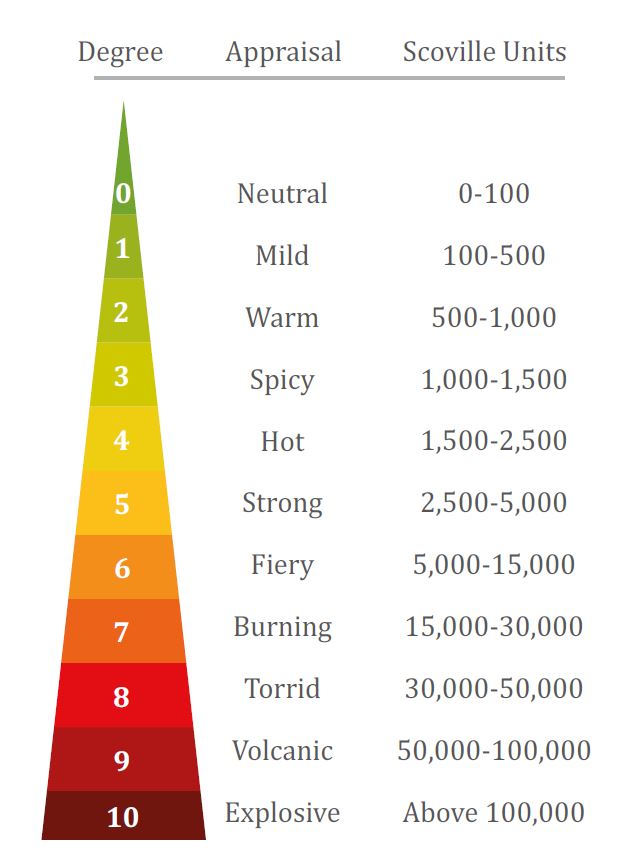
The Scoville Scale
It was pharmacologist Wilbur Scoville who invented the Scoville Scale in 1912 as a measurement to determine the heat level of peppers and chili peppers.
The heat level is generally linked to the capsaicin content in the pepper. To establish his classification, Wilbur Scoville would test a solution of pepper on five individuals. As long as the sensation of heat remained, he would increase the dilution. The score on the scale represents the level of dilution required to completely eliminate the spicy sensation.

Everything you need to know about peppers in videos.

The collection.
Amazon chilli pepper
The Amazonian pepper, originating from Colombia, is extremely hot. It is one of the spiciest peppers. Its fruity notes and subtle acidity resemble the Tabasco hot pepper. Its pale yellow color is due to its harvest before full maturity. In cuisine, it will enhance exotic sauce dishes or even dips.
Wiri wiri chilli pepper
Cousin of Cayenne pepper, originating from Guyana, the Wiri Wiri pepper is red and round. It grows vertically in a humid and hot climate at the edge of the tropical forest. Its resemblance to cherries has earned it the nickname "cherry pepper". Intensely flavored, it has hints of tomatoes. It should be used with caution to add fragrance to your stews, soups, and sauces.

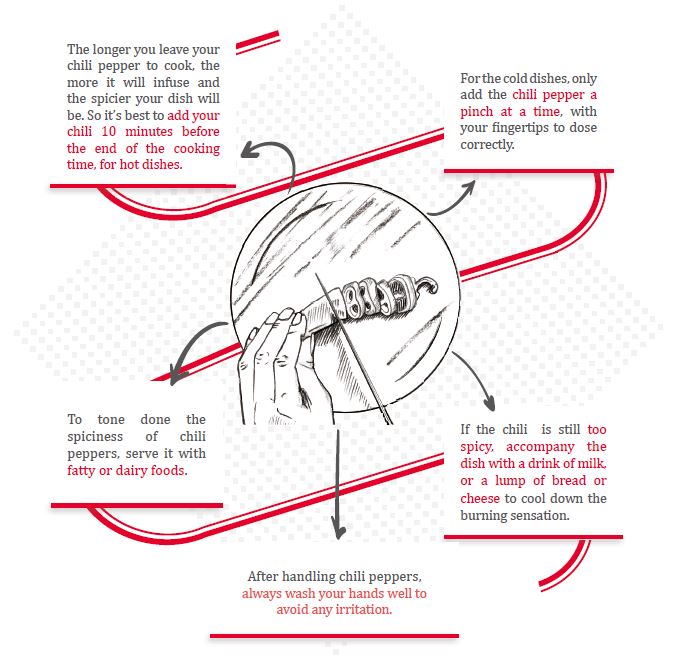
A few handy tips to get the best from your chili peppers:
The use of peppers in cuisine.

 Français
Français 









